Japan is highly susceptible to typhoons, which are a type of tropical cyclone similar to hurricanes. Due to its geographical location, Japan faces these storms frequently, especially from June to October, with peak activity occurring in August and September. Understanding the nature of typhoons, their impacts, and how to prepare for them is crucial for residents, tourists, and researchers alike. This comprehensive guide covers essential aspects of Japan’s typhoon season, from historical and economic impacts to safety tips and the role of climate change.
Understanding Typhoons in Japan
Typhoons, known as “taifu” in Japanese, are powerful tropical cyclones that form in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. They typically bring strong winds, heavy rainfall, and the potential for flooding and landslides. Japan’s location, straddling the Pacific Ocean’s typhoon belt, makes it particularly vulnerable to these storms. Each year, Japan experiences an average of 20 typhoons, with about three making landfall. The islands of Okinawa and Kyushu are especially prone to typhoon impacts due to their southern location.
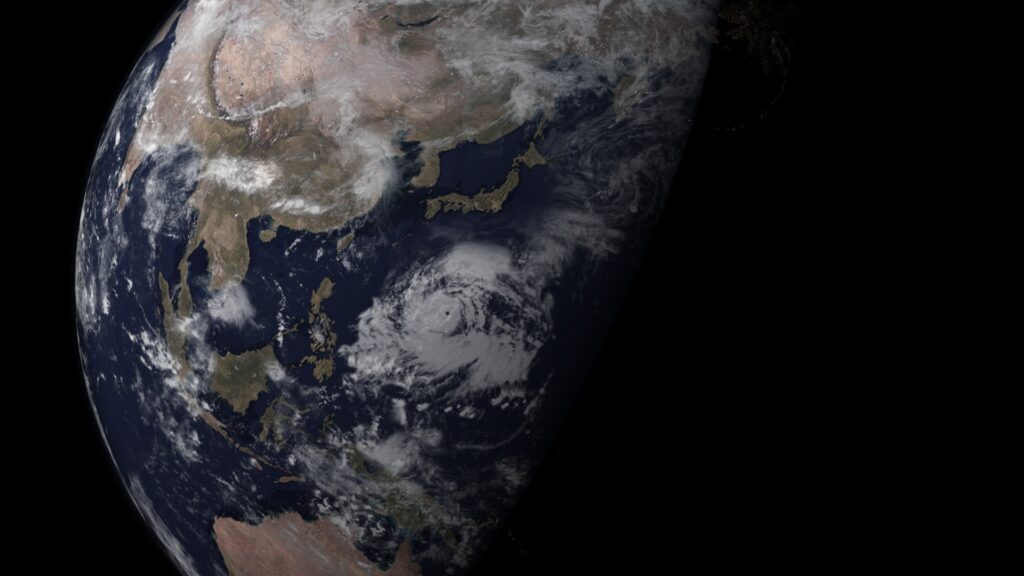

The typhoon season in Japan spans from June to October, with the highest activity usually seen between August and September. Typhoons often develop from tropical storms, gaining strength over the warm ocean waters before moving northward toward Japan. Factors such as sea surface temperatures, atmospheric pressure, and wind patterns influence their formation and trajectory.
Impact of Typhoons on Japan
Typhoons have historically had significant impacts on Japan’s infrastructure, economy, and daily life. These storms can cause widespread damage, including power outages, transportation disruptions, and destruction of homes and buildings. One of the most notable recent typhoons was Typhoon Hagibis in 2019, which resulted in severe flooding and landslides, leading to extensive property damage and numerous casualties. The economic cost of such events is substantial, often amounting to billions of dollars in recovery and reconstruction efforts.
Economic and Cultural Effects
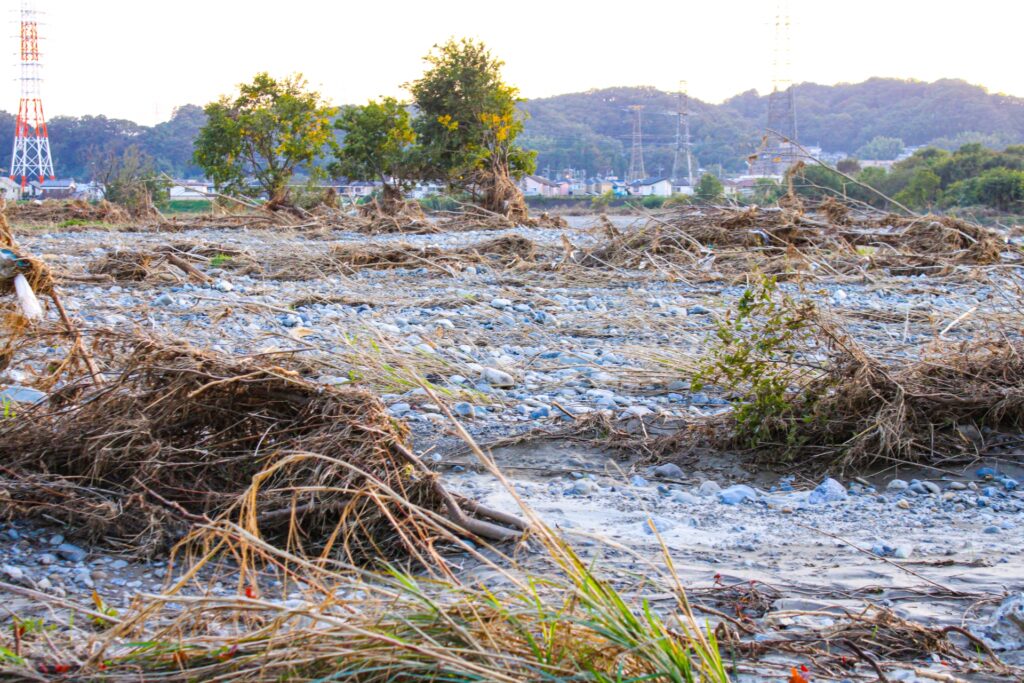

The economic impact of typhoons in Japan extends beyond immediate physical damage. The agriculture sector is frequently hit hard, with crops such as rice and fruits suffering significant losses due to flooding and strong winds. The tourism industry also takes a toll as travel plans are disrupted, and tourist attractions are closed for safety reasons. Additionally, typhoons have a cultural impact, influencing local customs, folklore, and community resilience strategies. In Japanese culture, typhoons are often seen as powerful natural forces, shaping the ways communities prepare and respond.
Japan’s Typhoon Preparedness Strategies
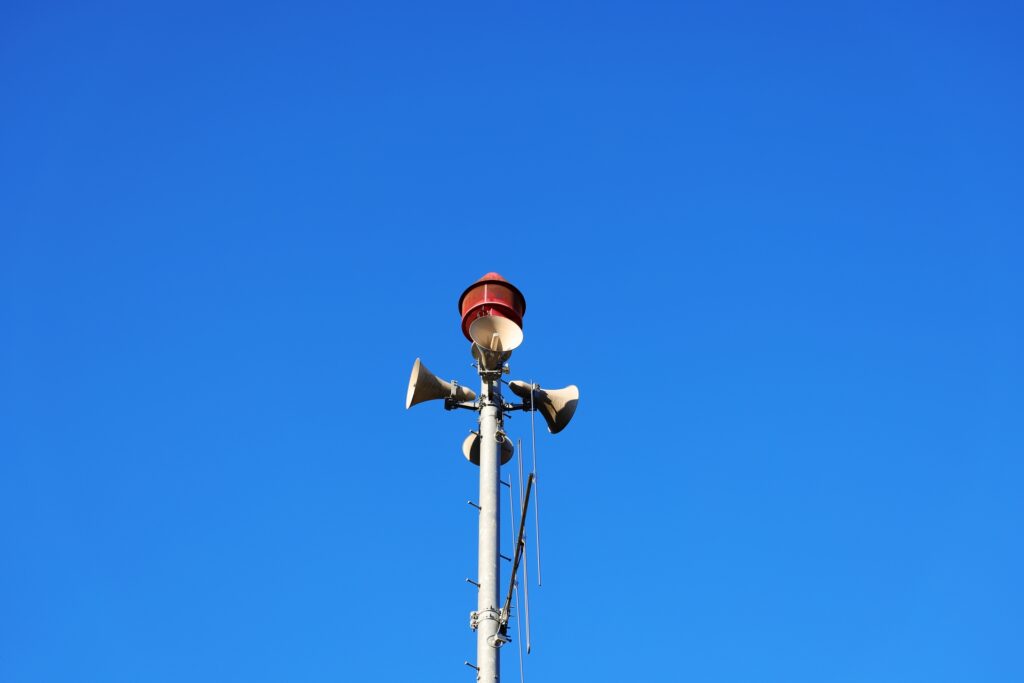

Japan is renowned for its advanced disaster preparedness and response strategies, which are crucial given the country’s frequent exposure to natural hazards. The nation employs a combination of technological advancements and community-based initiatives to mitigate the impact of typhoons. Early warning systems, such as satellite monitoring and Doppler radar, provide real-time data to forecast storm paths and intensities. These systems enable authorities to issue timely warnings and evacuation orders, minimizing casualties and property damage.
Technological Innovations
Japan’s commitment to technology plays a vital role in its disaster management strategies. Advanced meteorological satellites and sophisticated computer models help predict typhoon trajectories and intensity changes accurately. The country also uses real-time tracking and alert systems, which are accessible via mobile apps and online platforms, ensuring that both residents and visitors are informed about impending storms. These innovations have significantly improved Japan’s ability to respond to typhoons, reducing their overall impact.
Safety Tips for Residents and Visitors
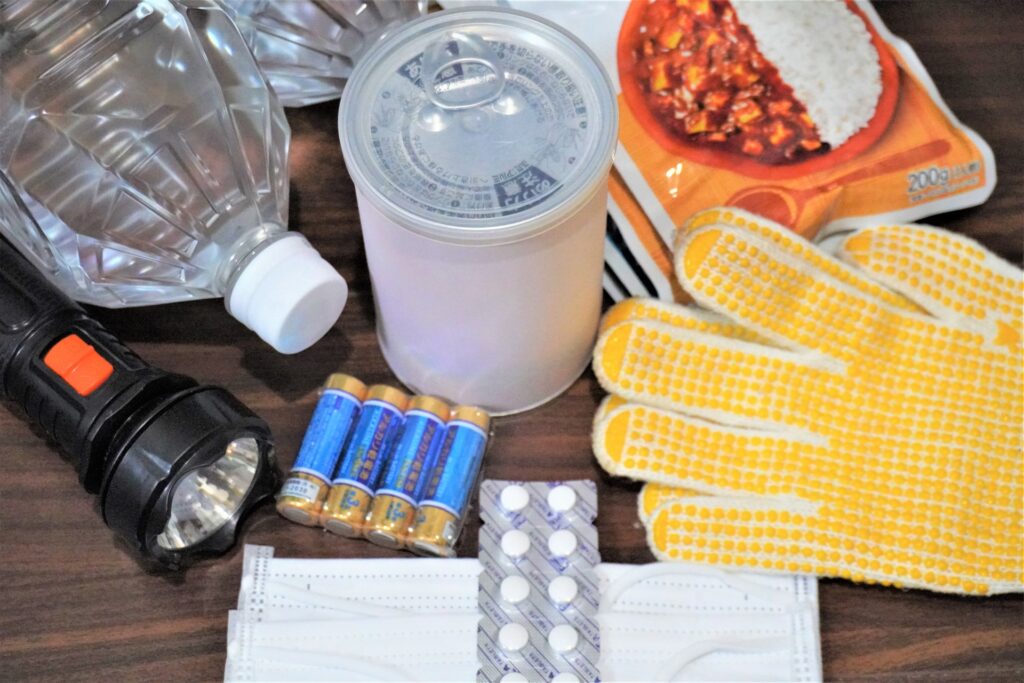

Whether you are a local or a tourist, knowing how to stay safe during typhoon season in Japan is essential. Preparing an emergency kit that includes food, water, medications, and important documents is crucial. It’s also advisable to stay indoors during a typhoon and avoid areas prone to flooding or landslides. Keep updated with the latest weather reports and follow instructions from local authorities regarding evacuations and safety measures.
Creating a Personal Emergency Plan

Having a personal emergency plan tailored to typhoon scenarios can save lives. This plan should include identifying the safest room in your home, knowing the location of the nearest evacuation center, and having a list of emergency contacts. For tourists, it’s important to familiarize themselves with hotel emergency procedures and local emergency numbers. Being prepared and having a clear action plan can significantly reduce the risk of injury or loss during a typhoon.
The Role of Climate Change in Typhoon Intensity
Climate change is increasingly influencing the frequency and intensity of typhoons in Japan. Warmer ocean temperatures provide more energy for typhoons, potentially leading to stronger and more destructive storms. Studies indicate that while the overall number of typhoons might not increase significantly, the intensity and rainfall associated with these storms are likely to grow. This trend poses a greater threat to coastal communities and requires enhanced adaptation and mitigation measures.
Scientific Predictions and Future Outlook
Scientific research predicts that climate change will continue to affect typhoon patterns, with an expected increase in the number of intense Category 4 and 5 typhoons. To mitigate these risks, Japan is investing in resilient infrastructure, improved early warning systems, and community education programs. Continued research and global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are essential to managing the future impacts of climate change on typhoons.
This comprehensive overview of Japan’s typhoon season highlights the importance of understanding, preparation, and adaptation in the face of these natural disasters. By following safety tips, leveraging advanced technologies, and addressing climate change, both residents and visitors can better navigate the challenges posed by typhoons in Japan.











