Japanese cities are famous for their compact yet efficient layouts, a product of centuries of urban planning that balances tradition with the needs of modern society. In this article, we will explore the key elements that define the structure of Japanese cities, from transportation systems to the use of green spaces and the integration of modern and traditional design principles.
The Influence of Traditional Design on Modern Japanese City Layouts
Japanese city planning is deeply rooted in tradition, particularly from the Edo period (1603–1868). The influence of traditional design principles, such as those seen in the arrangement of samurai districts and merchant quarters in cities like Kyoto and Edo (modern-day Tokyo), remains evident today. These older cities emphasized order, with residences and markets positioned strategically around central landmarks such as castles and temples.

Moreover, Zen gardens and Shinto shrines continue to shape the aesthetic and functional design of modern urban spaces. These traditional elements bring a sense of harmony and balance, blending green spaces into the otherwise dense, built-up environment. The clear separation between public and private spaces, combined with a focus on nature, has profoundly influenced how Japanese cities are structured in the present day.
Space Efficiency in Japanese Cities: The Key to High-Density Living
One of the defining characteristics of Japanese cities is their ability to manage space in highly efficient ways, especially given the limited land and high population density. This efficiency is achieved through a combination of vertical construction, micro-apartments, and multi-purpose buildings. In places like Tokyo, where land is scarce and expensive, urban planners have focused on creating space-efficient designs that maximize functionality without sacrificing comfort.

A key factor in this strategy is zoning regulations that prioritize mixed-use developments, allowing residential, commercial, and recreational spaces to coexist within the same areas. This approach fosters vibrant communities while minimizing the distance between home, work, and leisure, which is critical in a densely populated environment.

Public Transportation’s Role in Shaping Japanese City Layouts
Public transportation is the backbone of Japanese city layouts. In metropolitan areas like Tokyo and Osaka, the extensive and highly efficient subway and train networks not only provide a solution to traffic congestion but also influence the city’s expansion and zoning. The concept of transit-oriented development (TOD) plays a significant role, where high-density housing and commercial centers are built around major transit hubs.
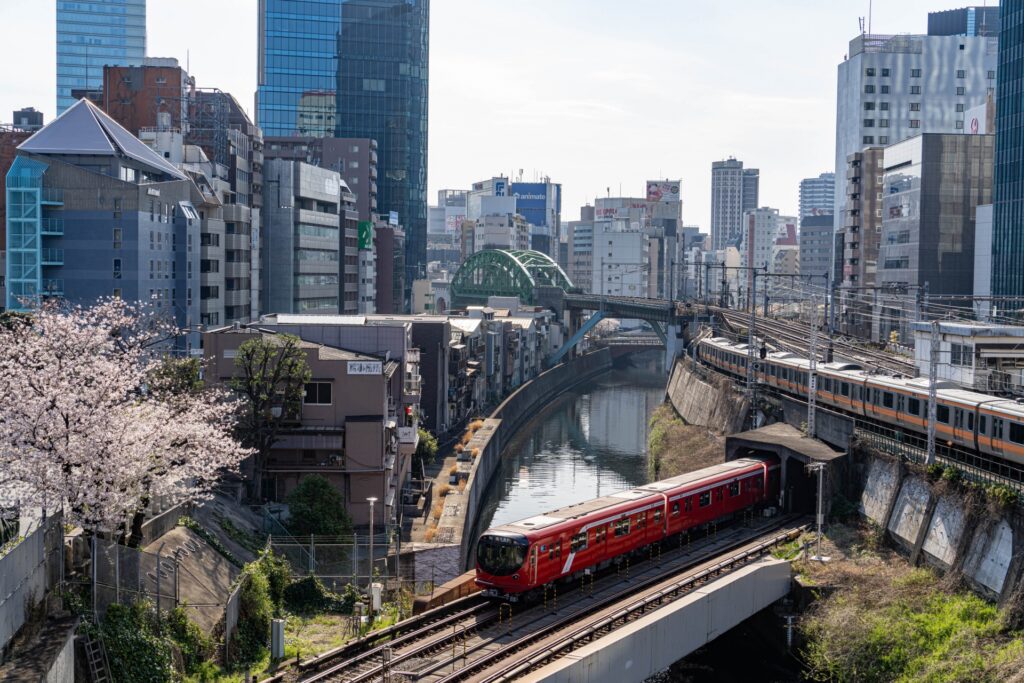

This design reduces the need for personal vehicles and promotes environmentally friendly transportation options, which helps contain urban sprawl. The regularity and punctuality of Japanese trains also allow cities to grow without sacrificing accessibility or convenience.
The Role of Green Spaces in Urban Planning
Despite their high population densities, Japanese cities place significant emphasis on green spaces. Public parks, traditional gardens, and nature reserves are meticulously integrated into urban landscapes. Green spaces not only improve the aesthetic appeal of cities but also provide much-needed recreational areas for residents.
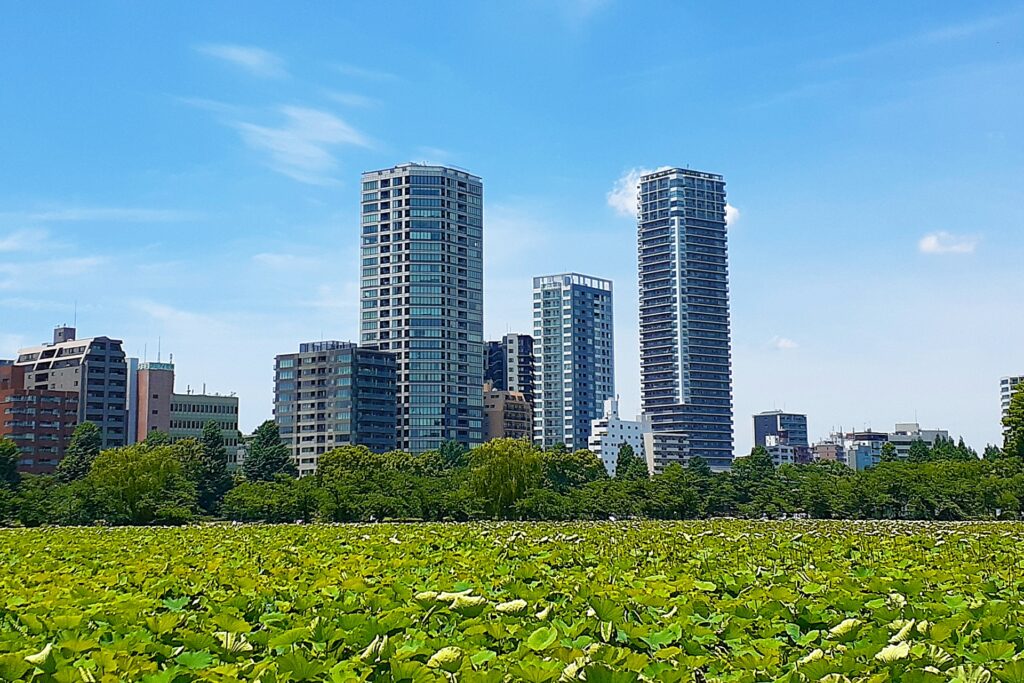

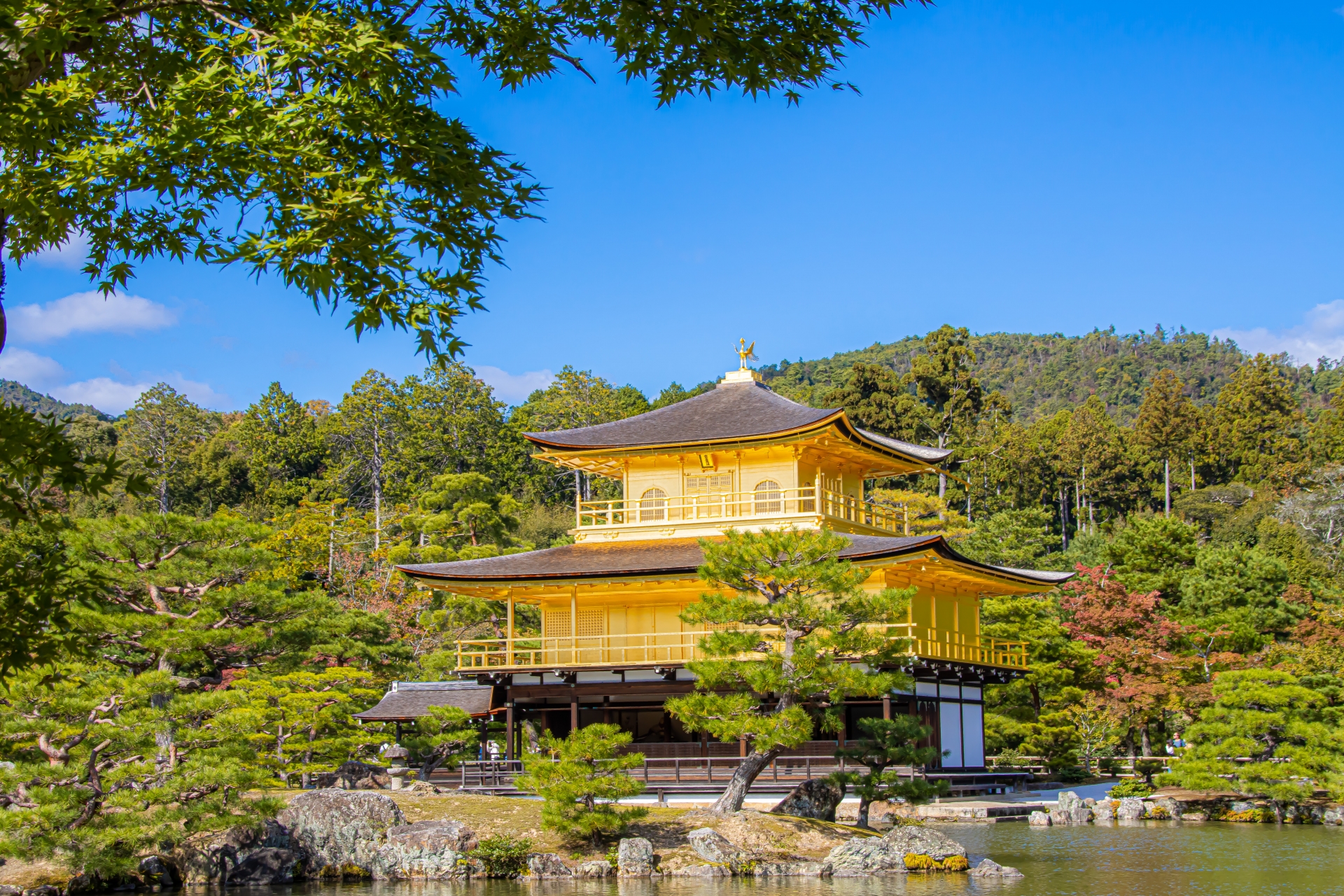
Traditional Japanese garden principles, such as the use of natural materials and attention to seasonal change, have influenced the design of modern parks. Spaces like Tokyo’s Ueno Park and Kyoto’s Kinkaku-ji (Golden Pavilion) offer serene environments amidst the bustling city, showcasing how nature is harmonized with urban life.


Sustainable Urban Design in Japanese Cities
Sustainability is a core principle in modern Japanese urban planning. Japanese cities, particularly Tokyo, have adopted eco-friendly building practices and renewable energy sources. Solar panels, rainwater harvesting, and energy-efficient building materials are increasingly used in new developments. Furthermore, cities incorporate smart water management systems to handle the demands of dense populations without stressing natural resources.
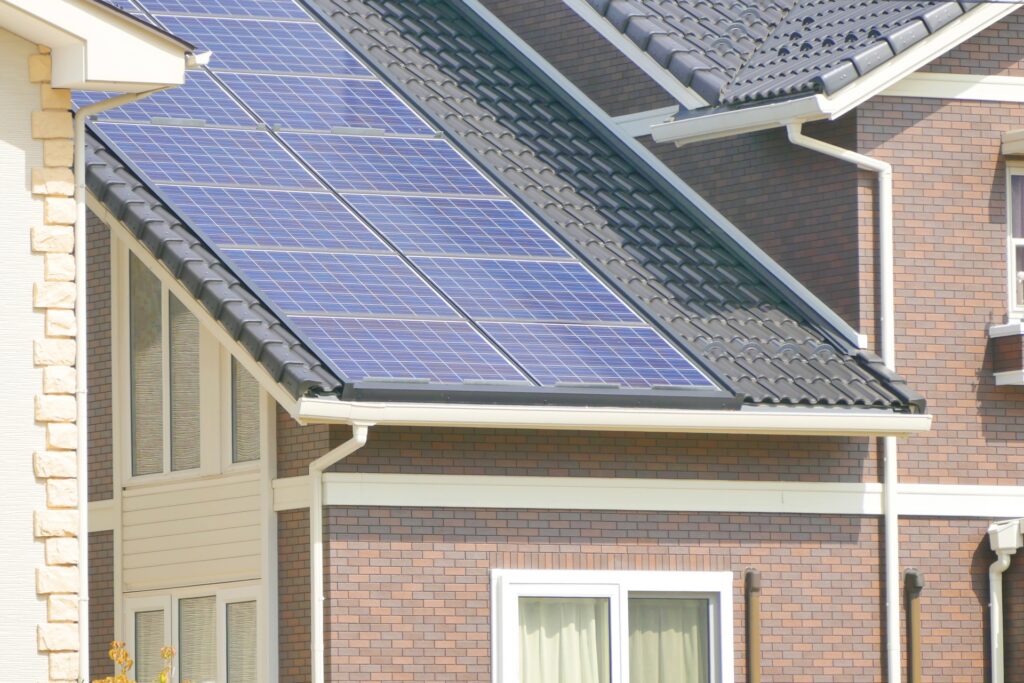

The Japanese approach to urban sustainability also includes waste management systems that promote recycling and minimize waste production. By focusing on both environmental and functional sustainability, Japanese cities are setting an example for efficient urban living.
Technological Innovations in Japanese City Planning
Looking toward the future, Japan is a global leader in incorporating technology into city planning. Smart city initiatives, such as those seen in Kashiwa-no-ha, utilize advanced technologies to optimize energy use, improve transportation efficiency, and enhance the quality of life for residents. Automation and AI play increasingly prominent roles in managing urban infrastructures, from traffic control to energy distribution.
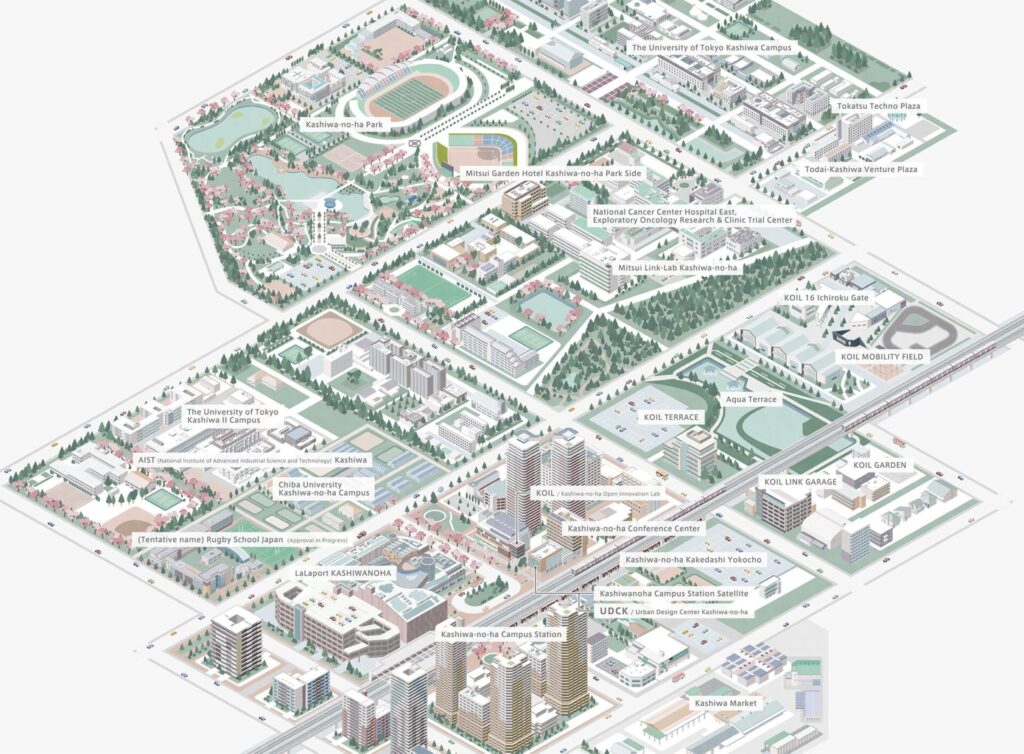
These technological innovations allow cities to function more efficiently, reducing the strain on natural resources while maintaining the high living standards that Japan is known for. This focus on smart urban planning is expected to shape the future of city layouts not only in Japan but around the world.
Reference: Kashiwa-no-ha Smart City
Conclusion
Japanese city layouts represent a unique blend of tradition and modernity, with a clear focus on efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life. Through the careful integration of public transportation, green spaces, and cutting-edge technologies, Japanese cities manage to thrive despite the challenges posed by limited space and high population density. These lessons from Japan’s urban planning offer valuable insights for cities worldwide seeking to create more livable and sustainable environments.











